Windows 2016 - ADFS 4.0¶
Getting this module to work is sometimes not so straight forward. If your not familiar with JWT tokens or ADFS itself, it might take some tries to get all settings right.
This guide tries to give a basic overview of how to configure ADFS and how to determine the settings for django-auth-adfs. Installing and configuring the basics of ADFS is not explained here.
ADFS server: https://adfs.example.com
Web server: http://web.example.com:8000
Step 1 - Configuring an Application Group¶
From the AD FS Management screen, go to AD FS ➜ Application Groups and click Add Application Group…
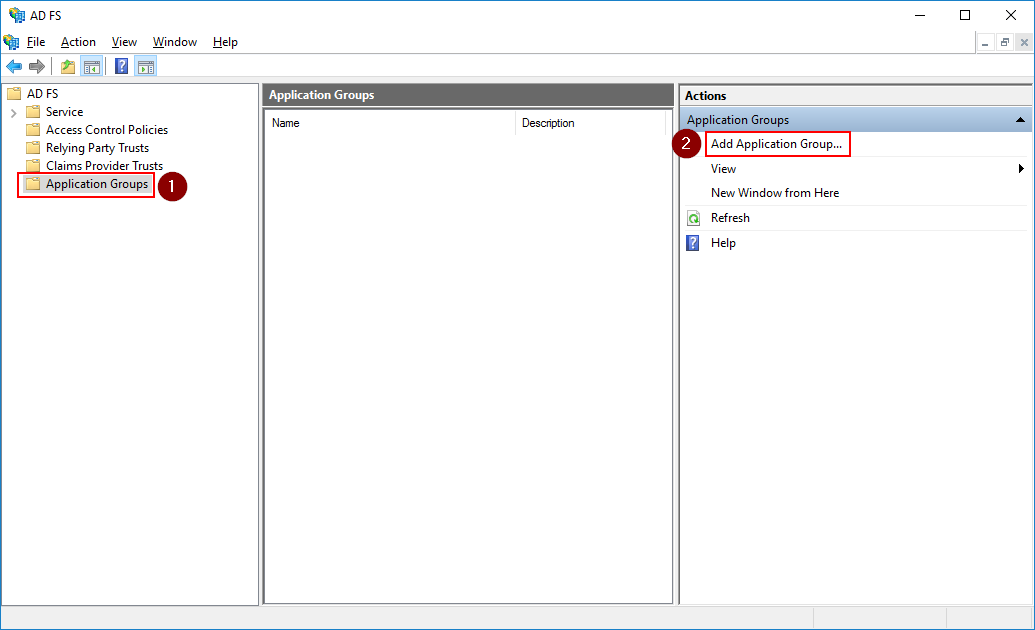
Fill in a name for the application group, select Web browser accessing a web application and click Next.
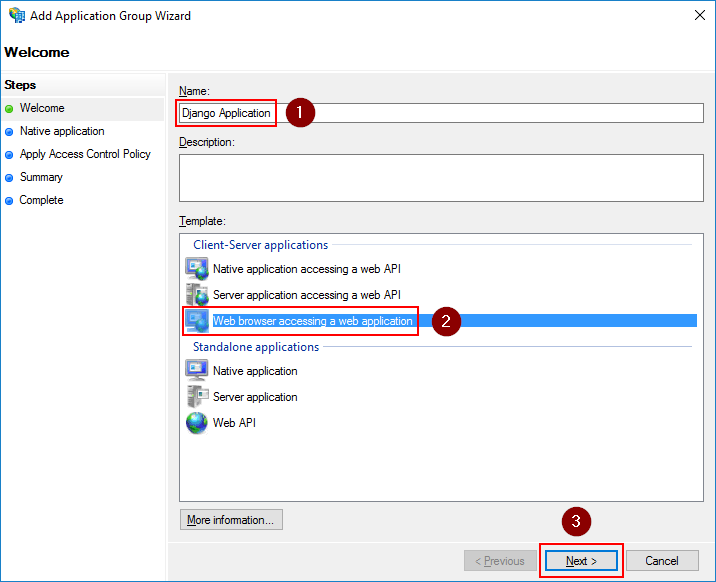
Make note of the Client Identifier value. This will be the value for the CLIENT_ID setting.
The Redirect URI value must match with the domain where your Django application is located and the patch where you
mapped the django_auth_adfs urls in your urls.py file. If you follow the installation steps from this
documentation, this should be something like https://your.domain.com/oauth2/callback.
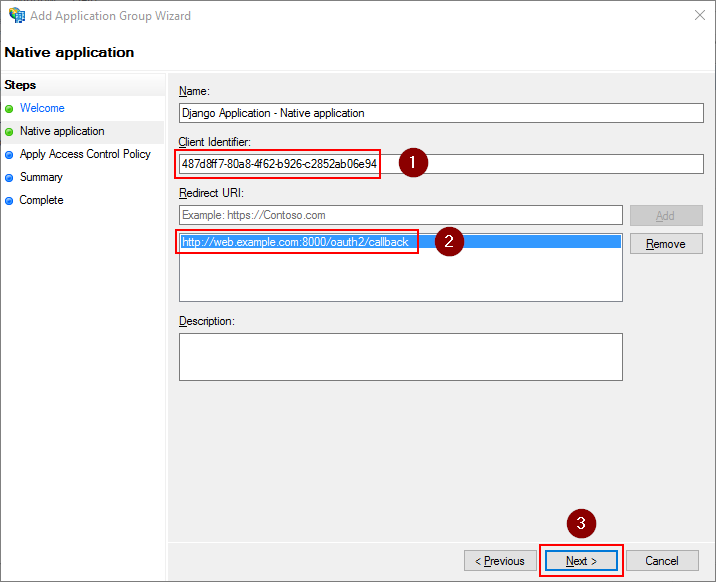
Select Permit everyone and click Next.
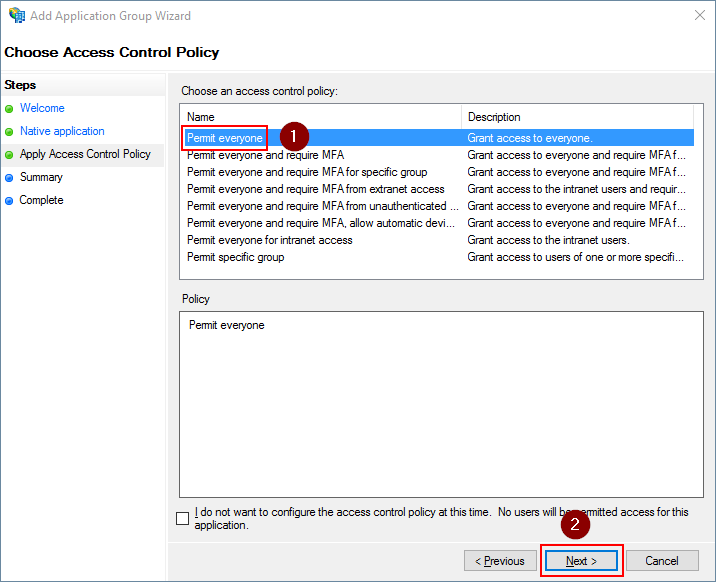
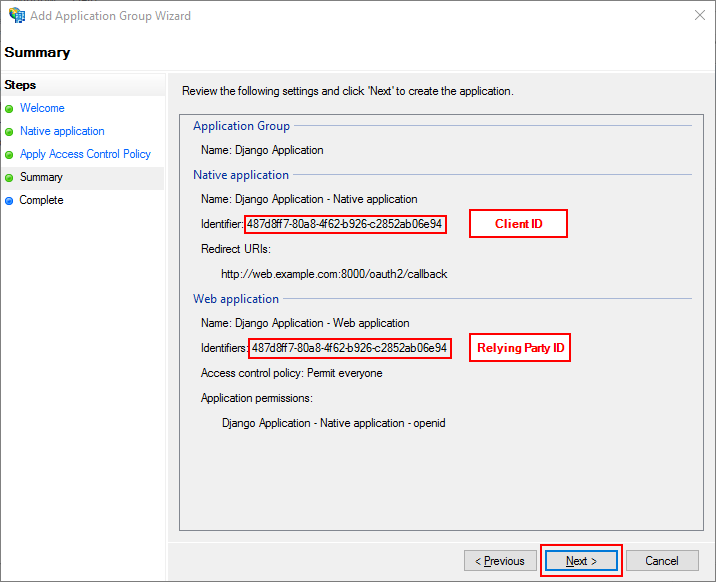
Review the settings and click Next
The Client ID is the value for the CLIENT_ID setting.
The Relying Party ID is the value for the RELYING_PARTY_ID and AUDIENCE setting.
While they both are the same in this screenshot, they can be changed independently from one another afterwards.
Close the wizard by clicking Close. Our django application is now registered in ADFS.
Step 2 - Configuring Claims¶
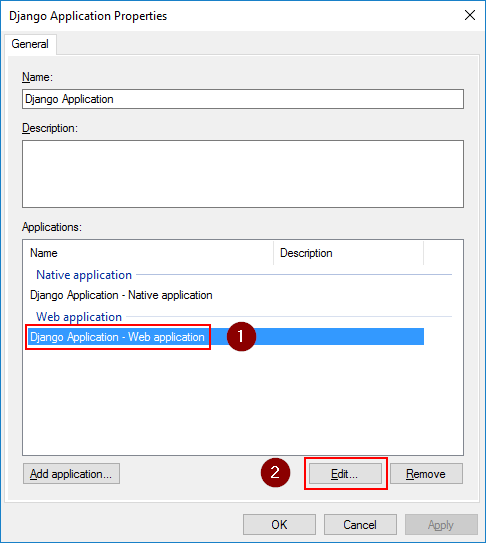
Open the properties for the application group we just created. Select the Web application entry and click Edit
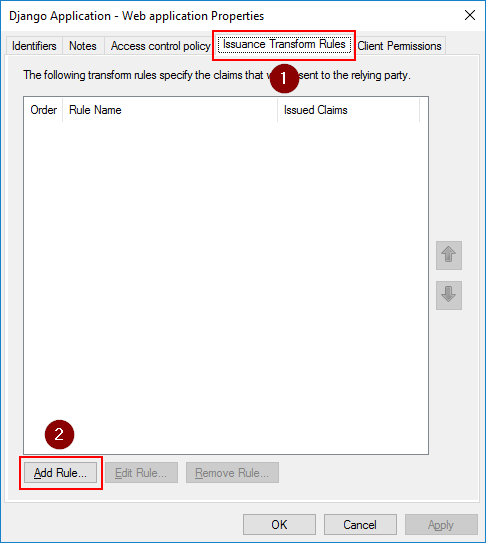
On the Issuance Transform Rules tab, click the Add Rule button
Select Send LDAP Attributes as Claims and click Next

Give the rule a name and select Active Directory as the attribute store. Then configure the below claims.
LDAP Attribute |
Outgoing Claim Type |
|---|---|
E-Mail-Addresses |
E-Mail Address |
Given-Name |
Given Name |
Surname |
Surname |
Token-Groups - Unqualified Names |
Group |
SAM-Account-Name |
Windows Account Name |
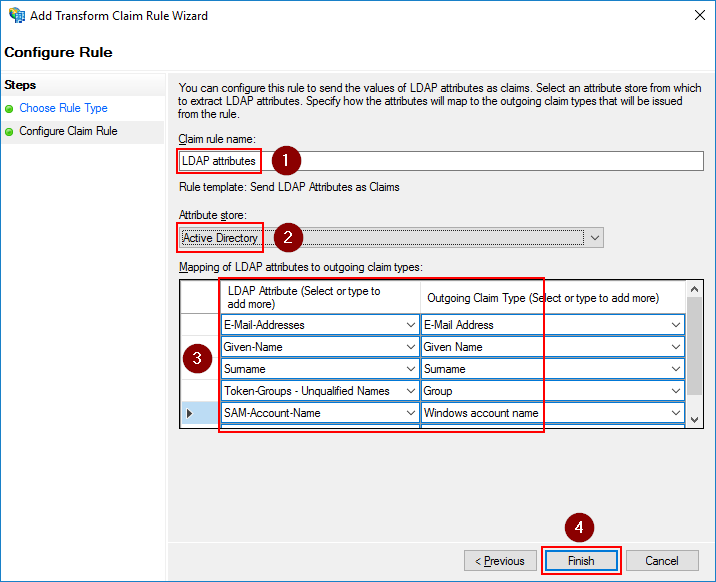
Click Finish to save the settings
Note
The Outgoing Claim Type is what will be visible in the JWT Access Token. The first 3 claims will go into the CLAIM_MAPPING setting. The 4th is the GROUPS_CLAIM setting. The 5th is the USERNAME_CLAIM setting.
You cannot just copy the outgoing claim type value from this screen and use it in the settings. The name of the claim as it is in the JWT token is the short name which you can find in the AD FS Management screen underneath AD FS ➜ Service ➜ Claim Descriptions
You should now see the rule added. Click OK a couple of times to save the settings.
Step 3 - Determine configuration settings¶
Once everything is configured, you can use the below PowerShell commands to determine the value for the settings of this
package. The <<<<<< in the output indicate which settings should match this value.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-AdfsNativeClientApplication
Name : Django Application - Native application
Identifier : 487d8ff7-80a8-4f62-b926-c2852ab06e94 <<< CLIENT_ID <<<
ApplicationGroupIdentifier : Django Application
Description :
Enabled : True
RedirectUri : {http://web.example.com:8000/oauth2/callback}
LogoutUri :
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-AdfsProperties | select HostName | Format-List
HostName : adfs.example.com <<< SERVER <<<
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-AdfsWebApiApplication | select Identifier | Format-List
Identifier : {web.example.com} <<< RELYING_PARTY_ID and AUDIENCE <<<
If you followed this guide, you should end up with a configuration like this.
AUTH_ADFS = {
"SERVER": "adfs.example.com",
"CLIENT_ID": "487d8ff7-80a8-4f62-b926-c2852ab06e94",
"RELYING_PARTY_ID": "web.example.com",
"AUDIENCE": "microsoft:identityserver:web.example.com",
"CLAIM_MAPPING": {"first_name": "given_name",
"last_name": "family_name",
"email": "email"},
"USERNAME_CLAIM": "winaccountname",
"GROUP_CLAIM": "group"
}
Enabling SSO for other browsers¶
By default, ADFS only supports seamless single sign-on for Internet Explorer. In other browsers, users will always be prompted for their username and password.
To enable SSO also for other browsers like Chrome and Firefox, execute the following PowerShell command:
[System.Collections.ArrayList]$UserAgents = Get-AdfsProperties | select -ExpandProperty WIASupportedUserAgents
$UserAgents.Add("Mozilla/5.0")
Set-ADFSProperties -WIASupportedUserAgents $UserAgents
After that, restart the ADFS service on every server in the ADFS farm.
For firefox, you’ll also have to change it’s network.automatic-ntlm-auth.trusted-uris setting
to include the URI of your ADFS server.